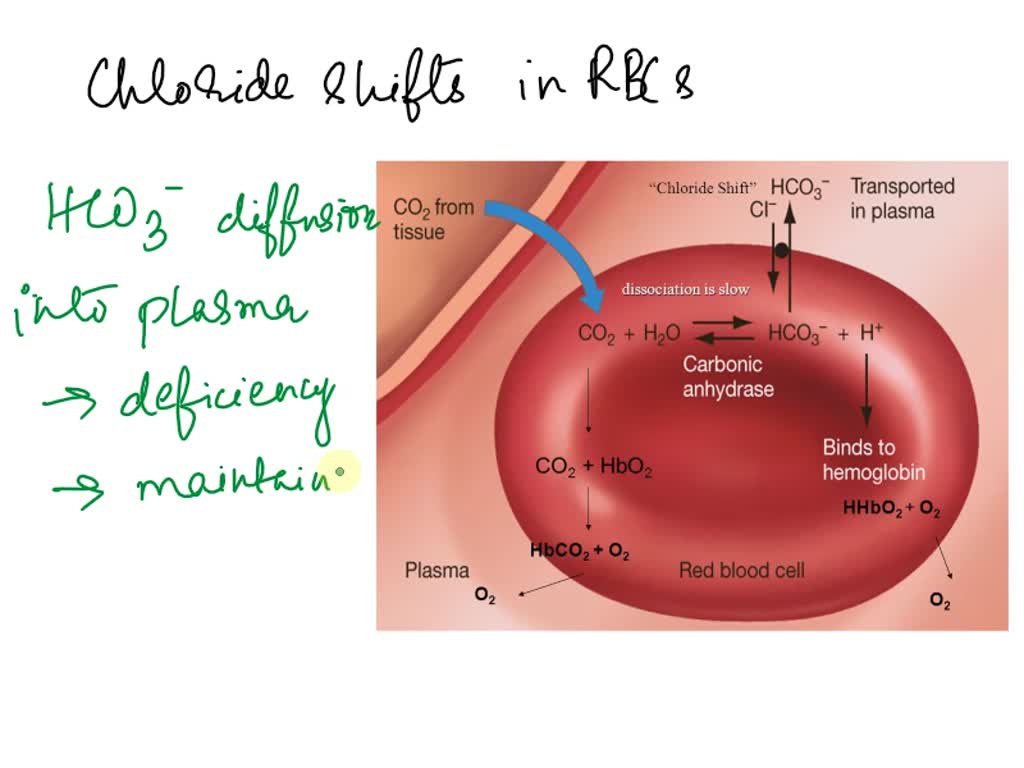
Chloride Ion Shift . Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form.
from www.numerade.com
The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen.
SOLVED the chloride shift in red blood cells is The movement of
Chloride Ion Shift Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride.
From www.youtube.com
CHLORIDE SHIFT YouTube Chloride Ion Shift Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.chegg.com
Solved A student wishes to determine the chloride ion Chloride Ion Shift Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of. Chloride Ion Shift.
From pozalevyduvo.cwiextraction.com
Le Chatelier S Principle Lab Cobalt Chloride Hexahydrate Chloride Ion Shift Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Module H Carbon Dioxide Transport PowerPoint Presentation, free Chloride Ion Shift Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood. Chloride Ion Shift.
From brainstuff.org
How does chloride shunting work in neurons? — Brain Stuff Chloride Ion Shift Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.youtube.com
CHLORIDE SHIFT HAMBURGER PHENOMENON YouTube Chloride Ion Shift Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood. Chloride Ion Shift.
From slideplayer.com
The Respiratory System ppt download Chloride Ion Shift Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
All‐Solid‐State Chloride‐Ion Battery with Solid Electrolyte Chloride Ion Shift Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.numerade.com
Inhibition of the chloride channel in the apical membrane of a parietal Chloride Ion Shift Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free download Chloride Ion Shift Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From stock.adobe.com
Hydrated Chloride Ion .Vector illustration Adobe Stock Chloride Ion Shift Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.learnatnoon.com
What is the role of Chloride Shift? Learn At Noon Chloride Ion Shift The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free download Chloride Ion Shift The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From byjus.com
When does the chloride shift occur? Chloride Ion Shift The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Part 2 Use your mouse to clickndrag a square around the Chloride Ion Shift Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED the chloride shift in red blood cells is The movement of Chloride Ion Shift Web the bicarbonate ion moves into the blood plasma to exchange itself with chloride ions to diffuse into the red cell with the hydrogen. Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web the loss of. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.learnatnoon.com
What is the role of Chloride Shift? Learn At Noon Chloride Ion Shift Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.
From www.onlinebiologynotes.com
Chloride shift/Hamburger phenomenon Online Biology Notes Chloride Ion Shift Web revision notes on 8.2.2 the chloride shift for the cie a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at. The movement of chloride ions (cl −) into red blood cells. Web the loss of anionic bicarbonate from the cell is compensated (maintaining electrical neutrality) by an influx of chloride. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form. Web the. Chloride Ion Shift.